SAP ERP Central Component (SAP ECC)
What is ECC?
SAP ERP Central Component (SAP ECC) is an on-premises enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. ERP integrates digital information that's created in one area of a business with data from other areas of the same business in real time. This means an update in one area of the business, such as sales, will trigger updates in related areas, such as inventory. Having a unified view of enterprise resources allows managers to make data-driven decisions that optimize core business processes.
SAP ECC is typically implemented in medium and large-sized companies and was developed for use in a wide array of industries ranging from pharmaceuticals, chemicals and steel to fast-moving consumer goods. It forms the foundation of SAP Business Suite, which also includes components, or modules, such as SAP Customer Relationship Management and Supply Chain Management.
SAP ECC vs. HANA, S/4HANA and SAP ERP
The SAP product landscape can be confusing. Here are the simplest answers to some common questions related to ECC.
What is the difference between SAP ECC vs. SAP ERP?
The term SAP ERP is SAP's catchall for its various ERP products, including ECC, S/4HANA, Business One and Business ByDesign.
What is the difference between ECC vs. HANA?
SAP ECC is an ERP system and Business Suite's core. ECC is an application suite that runs on a database, of which HANA is one example. HANA is SAP's in-memory database. When ECC is run on HANA it's called Suite on HANA. The full name is SAP Business Suite powered by SAP HANA.
What is the difference between ECC vs. S/4HANA?
S/4HANA is SAP's newest ERP product, and SAP ECC is its immediate predecessor. SAP ECC is still in widespread use as many companies have been reluctant to move to S/4HANA, largely because doing so is a massive undertaking. S/4HANA is not simply an upgrade of ECC, but instead a complete rewrite of it meant to take advantage of HANA.
What is the difference between ECC and R/3?
R/3 is ECC's predecessor. ECC is more akin to an evolution of R/3, unlike the relationship of S/4HANA to ECC.
ECC modules
SAP documentation officially changed from using the term module to using the term component when it moved from R/3 to SAP ECC, but many in the industry still use the term module.
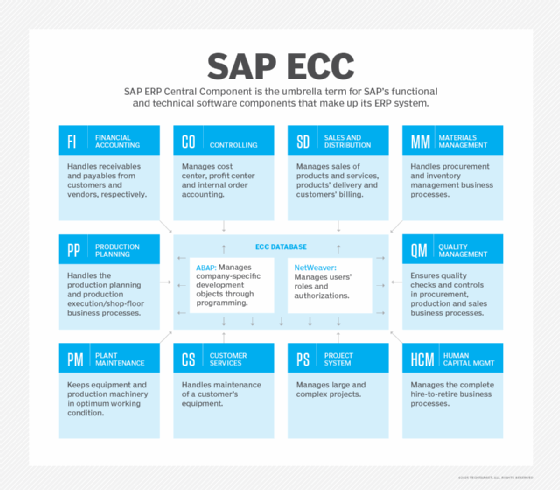
SAP ECC components have been integrated to work together. In general usage, both module and component refer to a part of the program that is independently developed to handle a targeted set of business processes (see figure). ECC is composed of 10 functional core components, or modules, and two technical components.
Below are frequently implemented functional modules that SAP ECC includes and the business functions they cover.
FICO
SAP FICO (SAP Finance and SAP Controlling) actually consists of two modules that, respectively, handle financial accounting and reporting, and cost planning and monitoring. Together they enable organizations to manage and store all of their financial data and transaction history in one place and run financial analytics.
Sales and Distribution (SD)
The SD module manages major processes of sales and distribution. This includes selling products or services through direct sales to customers or through distribution networks. SD also handles customer returns, along with billing and credit issuance.
Materials Management (MM)
The MM module manages procurement of materials and services from suppliers as well as related inventory processes, such as counting and reconciling physical inventory. MM also manages all goods issuance, receipts and transfers of a material from one plant or storage location to another.
Production Planning (PP)
The PP module helps businesses align demand with manufacturing capacity so they can plan product manufacturing, sales and distribution more effectively. PP plays a critical role in a manufacturer's supply chain and can be used for discrete, process or repetitive manufacturing or a combination of more than one type.
Quality Management (QM)
The QM module integrates extensively with procurement, production, sales and equipment maintenance processes. Advanced features include managing complete internal or external audits. QM can also assist in finding root causes of product failure to ensure ongoing quality improvements to a company's business processes.
Plant Maintenance (PM)
The PM module monitors machines and functional locations, such as a chiller room or boiler room, to ensure that they are in proper working order. It provides alerts when issues are detected to prevent machine failures and production disruptions. Business processes such as preventive, corrective and refurbishment maintenance are all covered in the SAP PM component.
Customer Services (CS)
The CS module handles the business processes for providing maintenance services to customer equipment. The option to bill customers for the maintenance services delivered is also part of CS.
Project System (PS)
PS is meant to manage large, complex projects such as setting up a new manufacturing plant or monitoring a plant's maintenance turnaround. Funneling all project-specific procurement or production through PS ensures that this module can allocate a project's costs correctly while keeping them within the budget.
Human Capital Management (HCM)
The HCM module manages HR-related functions. This includes payroll, time management activities such as attendance and leave, career development, travel and workplace safety. Functional modules have submodules that can be implemented as needed.
SAP ECC technical components
The technical components ABAP and NetWeaver were mandatory for an ECC implementation. The ABAP component supports custom development that is unique to a company. Companies used it to develop custom reports or specific reporting formats to cater to legal or financial reporting requirements.
The NetWeaver component is for system administration. It enables companies to assign specific roles and authorizations to individuals or groups.
SAP ECC implementation
SAP is intensely focused on S/4HANA. However, companies that implemented SAP ECC faced a major undertaking requiring the SAP-focused project implementation methodology known as the ASAP (Accelerated SAP). Major steps included the following: project preparation, creating a business blueprint of remodeled processes, ECC configuration and development, final preparation, and go-live and support.
Companies typically chose to implement the functional modules FICO, Materials Management and Sales and Distribution first, though they could choose which modules they wanted. For example, working with an SAP implementation partner, a customer may have decided it didn't need SAP Project System because it doesn't manage a large number of projects.
This level of choice and customization offered major flexibility but came with inherent complexity. SAP is trying to push companies to the cloud versions of S/4HANA, which standardizes offerings, though at the cost of flexibility. To compensate, it is also developing industry-focused versions of S/4HANA to match the flexibility traditionally offered by ECC.
Future of ECC
SAP is pushing companies to implement S/4HANA while promising to support ECC and other core Business Suite 7 applications until the end 2027, with optional extended maintenance until the end of 2030.







