Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH)
What is Remote Desktop Session Host?
Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) is a role in Remote Desktop Services (RDS). RDSH can host Windows session-based applications and desktops that can be shared with users remotely. Users can access this through a web client on a supported browser or through a Remote Desktop client, which runs on Windows, macOS, iOS and Android devices. To access applications or desktops remotely, users need to be on a network connection.
RDSH can be used for numerous reasons, such as for installing applications on a desktop in a remote location. This can become useful in organizations that need to help employees install a needed application while working remotely, for example.
The benefits of delivering Windows desktops or applications through RDSH instead of installing apps on employees' devices include quicker update rollouts and the ability for end users to access corporate apps and desktops remotely, using devices that wouldn't normally support those apps or Windows.
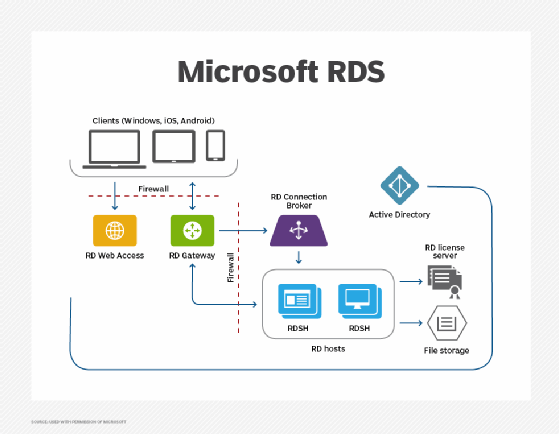
How RDSH works
Multiple end users can connect to the RDSH server through a remote desktop connection broker or Microsoft Azure to access session-based desktops, published applications and server resources. Multiple RDSH servers can be grouped together in a Session Collection and publish either Azure applications or session-based desktops, but not both from the same collection. The ability to group RDSH servers into collections was new to Windows Server 2012 RDS; the feature is useful for load balancing connections between connected servers.
RDSH uses a web portal to publish Windows desktops and applications to client devices. In addition, users can selectively publish desktops or applications to specific users and groups. To work properly, RDSH needs Internet Information Services (IIS) and a Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) connection. The HTTPS connection helps to provide an encrypted communications channel for the RD Web server and clients. Servers and clients also must have matching digital certificates, which need to match the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) that is used to access the RD Web Access.
Each remote session on an RDSH server needs a client access license (CAL). The Licensing role in RDS keeps track of those CALs, so there aren't more active sessions than licenses. Standard Windows Server licenses include the basic requirements for setting up and using RDSH and licensing services.