records management
What is records management?
Records management is the supervision and administration of digital or paper records, regardless of format. Records management activities include the creation, receipt, maintenance, use and disposal of records. In this context, a record is content that documents a business transaction.
Records are documents, such as contracts, memos, paper files, electronic files, reports, emails, videos, instant message logs and databases. Paper records are stored in physical boxes or file cabinets on premises or at a storage facility. Electronic records are stored on storage media in-house, off site or in the cloud.
How does records management work?
The goal of records management is to help an organization keep the necessary documentation accessible for both business operations and compliance audits. Spreadsheets are often used to track where records are stored.
Alternatively, software is available that uses both a taxonomy and a records retention schedule. Such software is marketed as enterprise information management (EIM) applications that can help an organization address information governance, which is the formal management of both records and other content.
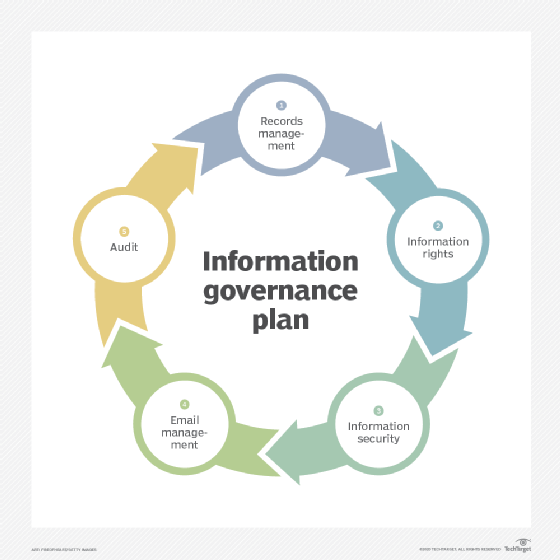
Records management is a key component of an information governance plan. The records management process involves the following five steps:
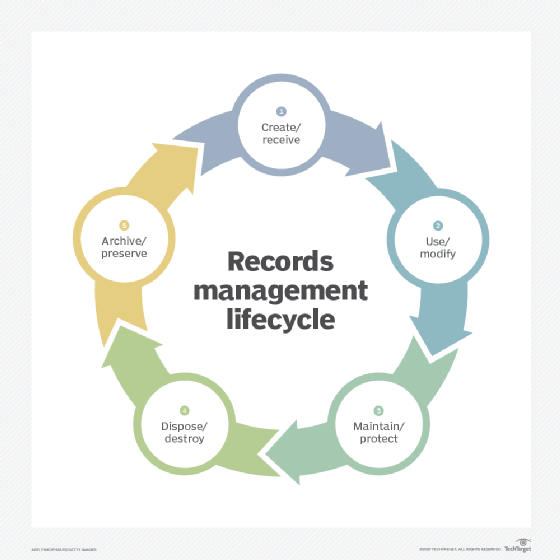
- Creating or receiving the records.
- Using or modifying the records.
- Maintaining and protecting records.
- Disposing and destroying records when they're no longer needed.
- Archiving and preserving permanent records or ones that need to be kept long term.
Why is records management important?
Records management ensures records are properly stored, accessed and managed in a secure manner. It also ensures compliance with legal requirements and regulations regarding the storage, access and use of information.
The following are specific reasons why records management is important:
- Historical knowledge. Proper record keeping lets organizations easily access past documents and track their progress over time. Historical records provide insights into how business operations have been conducted in the past as well. This helps businesses stay organized and make decisions based on historical data rather than relying on guesswork or intuition when planning for future strategies.
- Security. Records management prevents the loss of documents due to improper storage practices; this includes both physical destruction of paper-based files as well as digital records breaches, such as hacking attempts that could lead to confidential information being exposed online without authorization.
- Compliance. By having a system in place that complies all applicable laws related to document retention -- including those governing privacy rights -- businesses can protect themselves from fines and lawsuits resulting from mishandled documents.
- Access control. Effective recordkeeping systems gives organizations greater control over who has access to particular types of data. They can limit certain employee access based on job roles and responsibilities while simultaneously enforcing security protocols across multiple departments.
Pros and cons of records management
A records management program simplifies the process of identifying, locating and capturing paper and electronic documents that are related to specific topics, incidents or events. It makes it easier to retrieve specific documents covered by a legal action, such as a subpoena. It also assists in complying with regulatory and client requirements for content access and management.
Some of the downsides of records management include the following:
- Cost. The cost in terms of time and effort to set up a formal program can be high. In addition, automated records management systems as well as storage facilities, including file cabinets, records centers, storage media and cloud services, can be costly.
- Staffing. Finding the trained personnel to handle an organization's records management tasks and the complex systems involved can be difficult.
- Policies and procedures. Records and data retention policies must be developed to address issues related to document lifecycle, disposition of records, retention and disposition schedules, management of inactive records, and managing public records as well as business records.
Records management standards
ARMA International, which was originally called the Association of Records Managers and Administrators, is the largest global organization addressing records and document management. ARMA provides numerous services to members, including training, conferences, standards and best practices and professional certifications.
ARMA and IT professionals developed the Generally Accepted Recordkeeping Principles, a framework of eight principles for records management developed in 2009 and updated most recently in 2017. The eight principles are the following:
- Accountability to ensure senior management delegates authority for managing records to trained employees.
- Transparency to provide a program that's documented and available for review by all employees.
- Integrity to protect the accuracy, reliability and authenticity of records in the program.
- Protection to ensure records are secure and kept private and confidential.
- Compliance to make sure applicable laws, regulations and other requirements are met.
- Availability to ensure records can be made available when needed, including when disruptive events happen.
- Retention to guarantee that records are maintained for time frames required by law and industry standards and practice.
- Disposition to provide appropriate ways to get rid of records that are no longer needed.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developed two records management standards: Information and documentation -- Records management -- Part 1: Concepts and principles (ISO 15489-1) provides a detailed description of the various elements of records management and Information and documentation -- Guidelines for standards drafters (ISO 22310) provides guidance on how to establish and manage records management activities.
Learn about the seven stages of enterprise content lifecycle management and how business process management and content and records management intersect.






