Business Process Model Notation (BPMN)
What is Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN)?
Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN), also called Business Process Model and Notation, is an open standard to diagram a business process. It's like a flowchart and uses standardized graphics to represent the participants, choices and flow of the process. This kind of business process diagram is designed to be detailed, but easy to read without training.
These sorts of standard notations enable the same diagram to be used by executives, analysts and technical implementation staff to foster collaboration and understanding among groups. People with no programming experience can interpret this type of diagram. A BPMN diagram doesn't directly translate to any specific implementation, so it can be used universally for all an organization's business processes.
How is Business Process Modeling Notation used?
At its core, BPMN is a collection of symbols and rules on how to connect those symbols to represent a business process. These diagrams are referred to as a Business Process Model, and they can be used to diagram a public or private process. The original intent of the BPMN specification was to help bridge the communication gaps that often exist among various departments within an organization. BPMN is commonly used in business process management initiatives.
BPMN doesn't correlate to any specific workflow implementation, but it is often used to represent coded flows in a readily understandable way. For example, a business analyst may create the BPMN diagram a programmer uses to implement a business process using business process execution language (BPEL) in business orchestration software. The software can then generate a BPMN diagram of the implemented process for review by an executive.
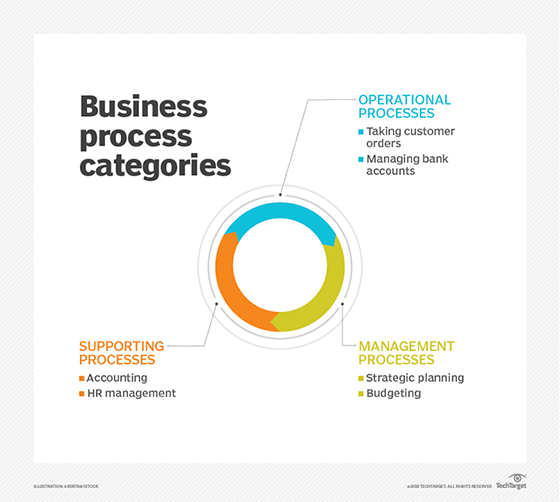
What are the benefits of Business Process Modeling Notation?
There are multiple reasons why BPMN and other graphical notations, such as Universal Process Notation, have practical value in enterprise settings. The benefits of BPMN include the following:
- Provides a common language. Different groups of people will use these diagrams to understand processes. BPMN diagrams make processes understandable by all business users and nontechnical groups as well as technical users like developers, programmers and other stakeholders.
- Adds clarity. A BPMN diagram encapsulates as much detail as possible about a business process. It explains everything that's needed to complete a process from start to finish and represents complex process semantics in a format that's easy to understand.
- Facilitates communication. BPMN diagrams convey explicit tasks with clear goals in mind. Technical developers, teams that carry out business processes and those involved in making business decisions can share them in ways that enhance communication.
Overview of Business Process Modeling Notation icons
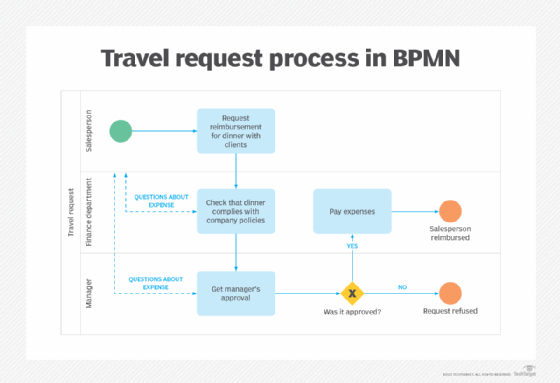
BPMN can be thought of as a graphic programming language. Each icon has a defined use and meaning in the diagram. The icons each represent a step or activity in the process.
Flow objects are connected to create the main sequence and to control the process flow. They are subdivided into events, activities and gateways.
- Events. These are represented by circles and indicate an interruption of a flow. Events are subdivided into start events, immediate events and end events.
- Activities. These are rounded rectangles and represent work done in a process. They can be atomic singular tasks or a compound process made up of another process flow.
- Gateway. Branching points in a flow are represented by diamonds. They can be exclusive decisions, inclusive decisions, branching parallel activities or complex gateways.
Connecting objects are directional arrows connecting flow objects to represent the sequence. There are three types of connecting objects: sequence flows, message flows and associations.
- Sequence flow. These solid lines show the order of objects that have only one source and one destination.
- Message flow. These dashed lines represent the flow of messages between participants.
- Association. This dotted line links artifacts with data objects. Data objects are data input, data output and intermediary information in a process, represented as a file with a folded corner. Artifacts are clarifying pieces of information, like a dashed box to represent a group with a note for text annotation, for example.
A swimlane is a container for separating activities. Swimlanes can be horizontal or vertical. There are two types of swimlanes: a pool and a lane. A pool is a box representing a separate entity, such as another department or business, which can be drawn without internal process representation as a black box for external participants. A lane is a box to partition within a pool to represent internal divisions. For example, it can represent roles in an organization, such as manager and associate.
History of BPMN and BPMN 2.0
BPMN was initially developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) in 2004. BPMI merged with the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2005, and it took over maintenance of the standard. BPMN 2.0 was released in 2011, under the name Business Process Model and Notation, but it kept the same acronym, BPMN. The latest version, released in 2014, is 2.0.2.
BPMN 2.0 includes a defined Extensible Markup Language (XML) interchange format. It also allows for different classes of diagrams including choreography and conversation diagrams. BPMN 2.0 introduced the choreography diagram as a means of depicting interactions that occur among all involved participants, with particular emphasis on the message flows. It introduced new icons specific to this type of process mapping diagram -- such as data object and data store -- to better represent how data flows through processes.
The conversation diagram visualizes conversation and messaging flows between participants from a bird's eye view and without a lot of specificity. In terms of technical updates, BPMN 2.0's XML capabilities provided a machine-readable format for mapping out business processes. Information about business processes could then be exchanged and easily understood by many types of software programs. Specifically, it offered two XML formats: XML Metadata Interchange and XML Schema Definition.
BPMN 2.0 is the core of an amalgam of standards known as BPM+ that OMG came out with in 2022. In addition to BPMN, these include Case Management Model, which describes how cases might work in workflow management, and Decision Model and Notation, which creates a standard notation for decision support. BPM+ is already being applied in healthcare, through an effort called BPM+Health.
BPMN's relationship with other standards
BPMN is a powerful tool for representing business processes and BPMN models, but it's limited in scope and requires the use of other standards for implementation or to capture other types of activities. For decision flows, Decision Model and Notation is recommended. And although BPMN contains standards for data objects, it doesn't capture all events in the data lifecycle, therefore, a data flow diagram is recommended.
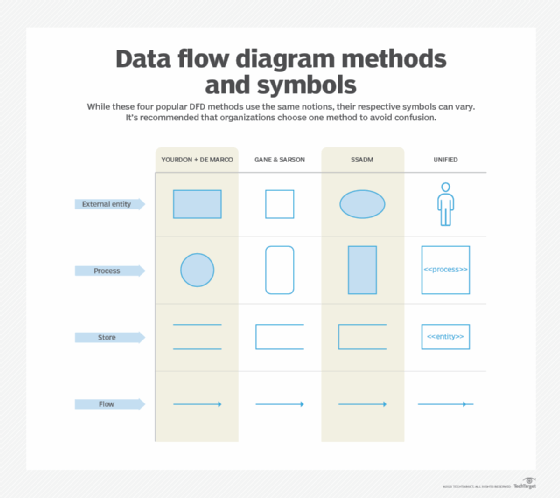
BPEL is an XML standard for orchestrating business processes for web services. There is no direct connection between BPEL and BPMN, but there are methods to map BPMN processes and flows into BPEL executable code. BPMN can help model a BPEL before it's implemented or help explain a BPEL flow.
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standard that helps software developers outline objects and relationships in software. BPMN can help developers capture needed information to create a complete UML model of software in development.
There are multiple business process modeling techniques used in business process design. Learn about nine important techniques with examples.






