Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI)
What is the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI)?
Established in August 2000, the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) is a nonprofit organization that promotes the standardization of common business processes, as a means of furthering e-business and business-to-business development. It has since merged with the Object Management Group (OMG).
BPMI was founded by a group of 16 e-business analysts and industry leaders, including the following:
- Aventail.
- Black Pearl.
- Blaze Software.
- Bowstreet.
- Cap Gemini Ernst & Young.
- Computer Sciences Corporation.
- Cyclone Commerce.
- DataChannel.
- Entricom Intalio.
- S1 Corporation.
- Versata.
- VerticalNet.
- Verve.
- XMLFund.
What is the history of the Business Process Management Initiative?
After its inception, the group grew to include more than 80 companies. BPMI's stated mission was "to promote and develop the use of Business Process Management (BPM) through the establishment of new standards for business process modeling, process design, deployment, execution, maintenance and optimization." By so doing, the BPMI methodology facilitates enterprise interoperability and further develops the global marketplace.
In 2005, BPMI and OMG merged, with OMG assuming control of the initiative and taking over the maintenance of BPMI's efforts. In 2011, OMG released Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) 2.0, establishing a more intricate standard for business process modeling.
Currently, e-business reflects the idiosyncratic ways that business processes work within an organization. There are, for example, redundant data, incompatible process flows and outdated management systems across organizations. Since BPMN doesn't lend itself to decision flows naturally, a decision flow chart approach known as the Decision Model and Notation standard has been added to BPMN since 2014.
The goal of the BPMI initiative -- and business process management today -- is to overcome these problems, and make it possible for business users across organizations to communicate more effectively, enhance data flow and share applications.
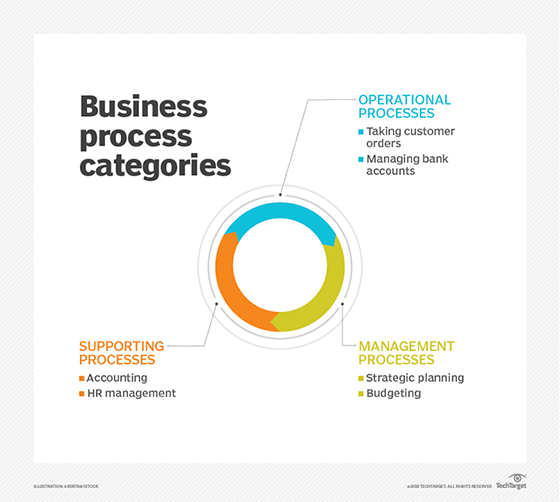
What are the components of BPMI?
The BPMI model of any two-way e-business process involves three main components: the public interface and two private configurations.
The public interface, which is the area of interaction between two business partners, is supported by various protocols such as those associated with BizTalk, electronic business extensible markup language (ebXML) and RosettaNet.
The model further defines two private setups, which are specific to the individual partners involved and can be described in any executable language. The Initiative specified such a language, as Business Process Modeling Language (BPML). BPML is an XML-based meta language that can be used to model components of business processes in the same way that XML can be used to model components of business data.
An associated query language, Business Process Query Language (BPQL) was developed by Initiative members as a standard management interface that can be used to deploy and execute defined business processes.
Both BPML and BPQL are open specifications. OMG continues to develop and promote open standards specific to particular e-business needs.
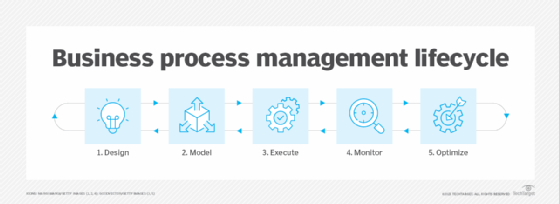
BPMN 2.0 elements and symbols
BPMN 2.0 is a standardized language for modeling business processes, using symbols grouped into four main categories to represent various process aspects.
The following are the four distinct elements and techniques that make up BPMN 2.0:
- Flows. These include events, activities and gateways.
- Connections. Connections include sequence flow, message flow and association.
- Swimlanes. These include pool or lane.
- Artifacts. These include data objects, groups and annotations.
BPMI and the OMG
BPMN is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a BPM. The merger of the BPMI and OMG includes the following business rules and BPM modeling tools:
- BPMI's Business Process Modeling Notation which can map to Unified Modeling Language or Business Process Execution Language (BPEL).
- OMG's Business Process Definition Metamodel.
- Business language, workflow vocabulary and rules.
- Business information management.
- Enterprise application integration.
- Web services processes such as WS-BPEL from OASIS, WSDL and XML Schema.
- Security management.
- Business Process Modeling Language.
- Business process query language.
Benefits of a BPMI
The specific benefits of business process management initiative depend on a business's specific goals, industry and configuration approach.
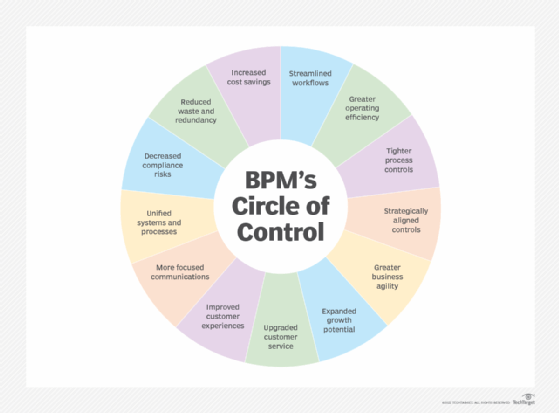
Common benefits of BPMI include the following:
- Standardization of business processes. The goal of BPMI is to encourage the standardization and optimization of common business processes, which can improve productivity, consistency and interoperability amongst enterprises.
- Enhanced productivity and operational efficiency. By streamlining activities, finding bottlenecks and encouraging cooperation, business process management initiatives enhance productivity and efficiency while lowering costs.
- Enhanced decision-making. By offering insights into process performance and pinpointing areas for improvement, BPMI's techniques and tools for modeling and evaluating business processes can improve decision-making.
- Enhanced organizational competitiveness. BPMI can assist organizations in becoming more competitive in their respective industries by streamlining and improving business processes.
- Automation and digital transformation. By digitizing processes, reducing costs, boosting agility and integrating business users and IT teams, BPM can be extremely helpful in digital transformation projects.
Examine the seven challenges that can obstruct the execution of effective BPM initiatives. Explore different approaches to overcome these challenges.






