availability zones
What is an availability zone?
Availability zones (AZs) are isolated data centers located within specific regions in which public cloud services originate and operate. Cloud computing businesses typically have multiple worldwide availability zones. This helps ensure cloud customers have a stable connection to a cloud service in the geographic zone that's closest to them.
Organizations select AZs for a variety of reasons, including compliance and proximity to customers. Cloud administrators can also choose to replicate services across multiple availability zones to decrease latency or protect resources. Admins can move resources to another availability zone in the event of an outage. Specific cloud services may also be limited to particular regions or AZs.
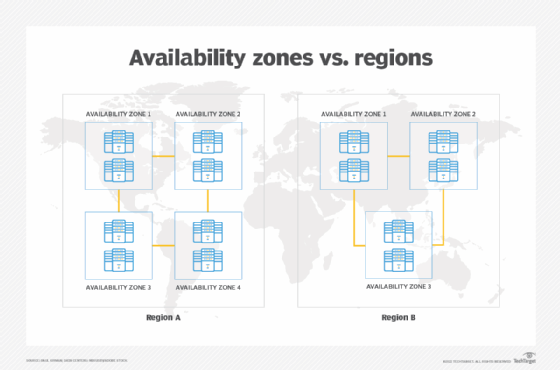
An availability zone consists of multiple data centers, which are all equipped with independent power, cooling and networking infrastructure all housed in separate facilities. A region can have multiple availability zones, but no availability zones are shared with different regions. Participating data centers in an availability zone connect to each other over a redundant, high-speed, low-latency private network link, and all zones in a region connect through the same sort of network links.
When an organization launches a cloud instance, it selects a region and then an availability zone. Normally, there are multiple availability zones customers can choose from in a region, or they can let the cloud service select their zone. Distributing instances across multiple availability zones provides redundancy and failover. This way, if one data center in an availability zone encounters a problem, the cloud provider can still offer its services through the remaining zones.
Differences between regions and zones
Availability zones are multiple, isolated locations within a region, and a region is a geographical location with multiple availability zones mapped within it. Every region is isolated and independent from every other region. Regions are spread out all over the world, so cloud providers can reach customers on multiple continents. Cloud providers typically have two or more availability zones within each region.
AWS, Azure and Google Cloud availability zones
The big three public cloud providers -- Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud -- use both regions and availability zones. The availability zones each cloud provider offers are also independent, so a failure or outage within one availability zone won't affect other zones; the other zones will pick up the slack from the region that went down. This ensures that an organization's disaster recovery plan isn't compromised.
Azure has the most supported regions and availability zones, followed by Google Cloud and then AWS as follows:
- Azure currently has more than 60 regions, some of which are in development. For each Azure availability zone, there's one or more data centers that can run independently. Azure regions are spread across the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Asia-Pacific.
- Google Cloud spans 34 regions and 103 availability zones, with nine other regions under development. Supported regions are spread across the Americas, Europe and Asia.
- AWS has 26 regions and 84 availability zones, with 24 additional availability zones under development. AWS regions are planned for Australia, Canada, India, Israel, New Zealand, Spain, Switzerland and the United Arab Emirates.
Choosing an availability zone
When choosing an availability zone from a cloud provider, users should consider the following:
- Latency and proximity. The closest zone will offer the lowest latency.
- Compliance. Depending on the location, cloud providers may need to meet different regulatory compliance laws and regulations, such as with GDPR.
- Service-level agreement. The level of availability may change depending on the cloud provider or region. Normally, AWS, Azure and Google Cloud provide high availability.
- Cost. Different regions may cost more than others, and the cost may change per cloud provider.
- Redundancy. Does the organization need data or apps stored in one location or across regions?
Learn more about how regions compare to availability zones in AWS in this article.







