A brief history of Google algorithm changes
Google frequently updates its algorithm to improve search result quality. These updates often enhance search query interpretation and prevent spam tactics.
As Google continuously changes its search algorithm, content marketers should be on their toes.
Google's search function filters through billions of webpages across the internet to find the best content to meets users' needs. To accurately interpret user queries and retrieve optimal results, Google relies on a complex set of rules known as an algorithm. Digital marketers and other content creators can use search engine optimization (SEO) strategies to understand Google's algorithm and create content around it to rank highly on the search engine results page (SERP) for target keywords.
An SEO strategy requires continuous re-evaluation because Google makes frequent changes to its algorithm each year. Google reportedly made 10 changes to its search engine in 2022 alone. Although some Google algorithm changes may be too small for content marketing teams to notice, others can dramatically affect SERP rankings.
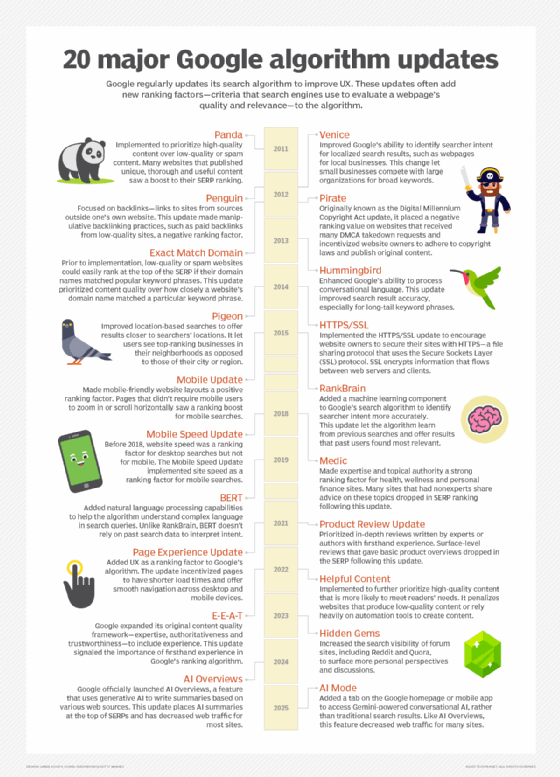
Major algorithm updates from the past decade include Panda, Pirate, Hummingbird, RankBrain, page experience update and helpful content system.
Why does Google change its search algorithm?
Google typically implements an algorithm change to improve its search function with different technologies or processes.
For instance, Google added bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) -- a deep learning tool -- to its algorithm in 2019 to improve its ability to understand conversational language. The BERT update offered users more relevant search results by more accurately interpreting searcher intent -- the purpose of a user's search query -- in lengthy and complex keyword phrases.
Google often makes updates to address aspects of its algorithm that people can manipulate. Before 2012, if a webpage's domain name exactly matched a particular keyword, that page could rank high on the SERP for that search term, even if its content was unhelpful to users. Spammers figured this out and filled domain names that matched popular search terms with low-quality content to generate web traffic. Then, in 2012, Google implemented the Exact Match Domain update to reduce the degree to which a site's domain name improved its SERP ranking.
Like any organization, Google wants its product to offer a positive UX. Therefore, it continuously updates its algorithm to meet user needs. Since the early 2000s, the company has made frequent changes to its algorithm annually. Digital marketers and SEO strategists should expect this pattern to continue and stay on top of future changes.